LC20 Conviction Insurance
Compare insurance quotes from specialist convicted driver insurance providers
Let insurance companies compete to offer you their best deal on your motor insurance!
DVLA Endorsement Code: LC20
(remains on driving licence 4 years from date of offence)
Learner Drivers | Licence Categories & Conditions
Power to Seize Vehicles | Vehicle Classification | Invalid Carriages | Types of Licence | Penalties
Driving Otherwise In Accordance with a Driving Licence
- It is an offence for a person to drive on a road a motor vehicle of any class otherwise than in accordance with a licence authorising him to drive a motor vehicle of that class.
- It is an offence for a person to cause or permit another person to drive on a road a motor vehicle of any class otherwise than in accordance with a licence authorising that other person to drive a motor vehicle of that class.
This means that any person who drives a motor vehicle or any person who permits or causes another person to drive a motor vehicle on a road of a class that that person is not authorised by a driving licence to drive will be committing the offence of driving otherwise in accordance with a licence or the offence of permitting or causing another person to commit this offence and will be liable to prosecution.
Any person driving a motor vehicle on a road without having a driving licence at all will also be committing this offence as will any driver who drives a vehicle otherwise in accordance with any conditions they must meet to drive that particular class of vehicle.
A driving licence is only valid when used in accordance with its conditions of issue.
There are a multitude of ways that a person may drive otherwise in accordance with a driving licence authorising them to do so and this page does not cover them all. It is recommended you check your legal entitlement to drive and any conditions that must be met if you are unsure.
Permitting or causing a person to drive otherwise in accordance with a licence
Any person who allows or causes another person to drive a vehicle on a road otherwise in accordance with a licence authorising that person to do so may be liable to prosecution.
The offence of causing and/or permitting another person to drive otherwise in accordance with a licence requires an element of mens rea. Mens rea is basically a persons awareness of the fact that his or her conduct is of a criminal nature.
Learner Drivers (provisional licence holders)
Learner Car Drivers
Learner car drivers who drive a car on a road without displaying L plates (or D plates in Wales) will be guilty of driving otherwise in accordance with a driving licence, as will learner car drivers who drive without supervision.
Learner Motorcycle Riders
Similarly learner motorcycle riders who ride a motorcycle unaccompanied by an approved DSA motorcycle instructor on a road without first passing a CBT test will be guilty of driving otherwise in accordance with a driving licence, as will learner motorcycle riders who have passed a CBT test but fail to display L plates (or D plates in Wales).
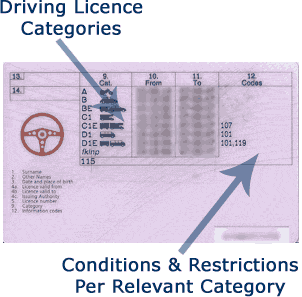
Driving licence categories and conditions that must be met to legally drive
The categories of vehicle that a licence holder is entitled to legally drive will be clearly marked on their driving licence as shown below (section 9).
A driving licence is only valid if used in accordance with any relevant conditions and restrictions. The codes for the relevant conditions and restrictions for a particular category of vehicle will appear in section 12 of a driving licence alongside that particular category as shown below. If in doubt then please contact the DVLA for clarification or view your driving licence information online.
VIEW YOUR DRIVING LICENCE INFORMATION ONLINE
(find out what classes of vehicles you can legally drive)
DRIVING LICENCE CATEGORIES (GOV.UK) | DRIVING LICENCE CODES
Power to Seize vehicles driven without a licence to do so
s. 165A of The Road Traffic Act 1988 [1] gives police officers the power to seize motor vehicles driven on a road without a licence or motor vehicles of any class driven on a road otherwise in accordance with a licence.
Police officers can immediately access and check information of official records pertaining to driving licences held by individuals.
The power to seize vehicles is more likely to be exercised when there is no record of an appropriate licence being held by the driver and a valid driving licence and counterpart is not produced.
What is classed as a motor vehicle?
(c)
...
"motor vehicle" means, subject to section 20 of The Chronically Sick and Disabled Persons Act 1970 (which makes special provision about invalid carriages, within the meaning of that Act), a mechanically propelled vehicle intended or adapted for use on roads
...
The aforementioned act lists and defines mechanically propelled vehicles such as motor cars, heavy motor cars, motor tractors and motor cycles. However there are other vehicles which have been examined by courts and found to be classed as motor vehicles which require a licence to drive on a road.
These include:
Go-ped
A go-ped is a small scooter used by people who stand on a two-barred sub-frame. The propulsion of this scooter is assisted by a 22.5 cc engine. The divisional court ruled that the go-ped was in fact classed as a motor vehicle for which any person riding it required a licence.
Mini-moto
A mini-moto is a motor vehicle which is propelled by a petrol engine, has motorcycle tyres and an exhaust system. It is classed as a mechanically propelled motorcycle, albeit a very small one, which requires a licence to ride/drive as is any other mechanically propelled vehicle, not being an invalid carriage which has less than four wheels and an unladen weight not exceeding 410kg.
City mantis electric scooter
A city mantis electric scooter is a vehicle with a battery operated motor that is electronically propelled and is capable of travelling at a speed of 10mph. This electronic scooter is classed as a motor vehicle requiring a licence to drive.
For a mechanically propelled vehicle to be classed as a motor vehicle within the Traffic Acts definition of a motor vehicle then it must be a vehicle which was intended or has been adapted for use on a road.
INVALID CARRIAGES NOT CLASSED AS MOTOR VEHICLES
Use of invalid carriages on highways.
- In the case of a vehicle which is an invalid carriage complying with the prescribed requirements and which is being used in accordance with the prescribed conditions—
- no statutory provision prohibiting or restricting the use of footways shall prohibit or restrict the use of that vehicle on a footway;
- if the vehicle is mechanically propelled, it shall be treated for the purposes of The Road Traffic Regulations Act 1984 and The Road Traffic Act 1988, except section 22A of that Act (causing a danger to road users by interfering with motor vehicles etc.), and The Road Traffic Offenders Act 1988 as not being a motor vehicle; and sections 1 to 4 [Causing death by dangerous driving, dangerous driving, careless and inconsiderate driving, driving or being in charge when under the influence of drink or drugs], 21 [Prohibition of driving or parking on cycle tracks], 34 [Prohibition of driving mechanically propelled vehicles elsewhere than on roads], 163 [Power of police to stop vehicles], 170 [Duty of driver to stop, report an accident and give information and documents] and 181 [General provision as to accident inquiries] of The Road Traffic Act 1988 shall not apply to it and
- whether or not the vehicle is mechanically propelled, it shall be exempted from the requirements of section 83 [Offences to do with reflectors and tail lamps] of The Road Traffic Act 1988
s. 20 of The Chronically Sick and Disabled Persons Act 1970 [2] defines an invalid carriage as a vehicle, regardless as to whether or not it is mechanically propelled which is constructed or adapted for use for the carriage of one person. That person using the vehicle being a person suffering from some physical defect or disability.
This means that a person driving/riding an invalid carriage who suffers from some kind of physical defect or disability that requires the use of said carriage does not need a licence to drive/ride it as it is exempt from being classed as a motor vehicle as defined under s. 185 of The Road Traffic Act 1988 [1].
Different Types of driving licence
Great British Driving Licence:- Is actually a domestic licence commonly referred to as a Great Britain Domestic Licence or simply a British driving licence.
Convention Driving Permit:- Is a driving permit issued under the authority of a country outside the United Kingdom to a person who has given proof of their competence to drive. A convention driving permit is commonly known as an 'International Driving Licence'.
Domestic Driving Permit:- Is a driving permit issued under the law of another country authorising the permit holder to drive a motor vehicle or a specified class of motor vehicle in that country.
British External Driving Licence:- Is a driving licence issued under the law of the Isle of Man or any of the Channel Islands that are not part of Great Britain, the UK or the EEA.
Community Driving Licence:- Is a driving licence issued in an EEA state (other than Great Britain or the UK) authorising the holder of the licence to drive a motor vehicle of that class.
The rules governing a persons legal entitlement to drive in Great Britain are complicated and depend on numerous factors including whether a person is a foreign visitor or a foreigner who takes up residence in Great Britain.
Non-resident foreigners In Great Britain / THE UK
Find out if you can legally drive in Great Britain with your non-GB licence (GOV.UK)
Foreign Visitors Temporarily driving in Great Britain
Please use the link above to clarify whether you can legally drive and what class of vehicles you may legally drive as a visiting foreigner to Great Britain.
The Motor Vehicles (International Circulation) Order 1975 [3] makes provisions for foreigners who are resident outside of the UK who are temporarily in Great Britain to legally drive for a period of up to 12 months from the date of their last entry into the UK if they hold a valid convention driving permit or a valid domestic driving permit authorising that person to drive the vehicle in question. However there may be certain restrictions, please see the important note below.
A foreigners legal entitlement to drive is of course presuming they are not disqualified from holding or obtaining a driving licence either by conviction, by order of a court, by age or for any other reason.
Temporarily is not simply just a time limit. It means a casual presence in the UK for reasons such as a holiday or in the case of certain drivers a visit due to work related requirements. This is in contrast to a more permanent form of residence such as a foreign student studying in Great Britain.
IMPORTANT NOTE: There may be certain restrictions on the class of vehicle/s certain foreigners are authorised to drive temporarily in Great Britain despite the fact their convention or domestic driving permit authorises them to drive a particular class of vehicle in other countries. This will depend on what country their driving licence was issued, what country the vehicle in question is registered, the purpose of their temporary visit to the UK and whether or not they drove the vehicle in question into Great Britain.
It is very important for any foreign visitor with a non-GB licence to clarify the classes of vehicle they can legally drive while temporarily visiting Great Britain by using the driving in GB on a non-GB licence tool provided by www.gov.uk and/or contacting the DVLA directly. Otherwise they may be liable to prosecution for driving otherwise in accordance with a licence.
Resident foreigners in Great Britain
Find out if you can exchange your foreign licence for a British licence (GOV.UK)
The Motor Vehicles (Driving Licences) Regulations 1999 [4] makes provisions for people who live abroad and take up residency in the UK.
Foreigners that hold a relevant foreign driving licence/permit who move to the UK and become British residents may be able to exchange their non British driving licence/permit for a British driving licence after taking up residence.
The rules governing foreign driving licence exchange are complicated and depend on numerous factors including:
- The type of driving licence they have: car licence, motorcycle licence, lorry licence, bus licence or minibus licence etc.
- Their age and the date their driving licence was issued
- The country in which their foreign driving licence was issued, there are different rules concerning different countries including:-
- The European Union
- Northern Ireland
- Jersey, Guernsey or Isle of Man
- A designated country who have exchange agreements with Great Britain, these include: Andorra, Australia, Barbados, British Virgin Islands, Canada, Faroe Islands, Falkland Islands, Gibraltar, Hong Kong, Japan, Monaco, New Zealand, Republic of Korea, Singapore, South Africa, Switzerland and Zimbabwe
- Any other country
IMPORTANT NOTE: There are different time limits in which foreigners who become resident in Great Britain can and/or are required to exchange their foreign driving licence depending on their particular circumstances and the driving licence/permit they currently hold.
It may be that they can only drive temporarily in Great Britain before they are required to take a theory and practical driving test in order to obtain a Great Britain driving licence.
It may be that they can only drive temporarily in Great Britain before they are required to exchange their non-GB licence for a GB licence.
It may be that they must stop driving certain classes of vehicle until a relevant theory and practical driving test is passed in order to obtain a Great Britain driving licence for that particular class of vehicle.
It may be that they must register with the DVLA and provide specified information within a certain time period.
It may be that a combination of the above apply.
It is very important for foreigners who become resident in the UK to clarify their legal entitlement to drive in Great Britain and the requirements for their continued legal entitlement to drive in Great Britain.
This can be achieved by using the exchange a foreign driving licence tool provided by www.gov.uk and/or contacting the DVLA directly. If they fail to check their legal entitlement to drive in Great Britain then they may be liable for prosecution for driving otherwise in accordance with a licence.
Penalty for driving otherwise than in accordance with a licence
The courts have the discretion to impose a driving disqualification upon any person convicted of driving otherwise in accordance with a driving licence if that person did not have a driving licence and their driving would have not been in accordance with any driving licence that could have been issued to them.
The maximum penalty upon conviction of driving otherwise in accordance with a driving licence is a fine not exceeding Level 3 (£1,000) and the endorsement of 3 - 6 penalty points which remain on a driving licence for 4 years from the date of the offence.
Reference:
[1] The Road Traffic Act 1988[2] The Chronically Sick and Disabled Persons Act 1970[3] The Motor Vehicles (International Circulation) Order 1975[4] The Motor Vehicles (Driving Licences) Regulations 1999